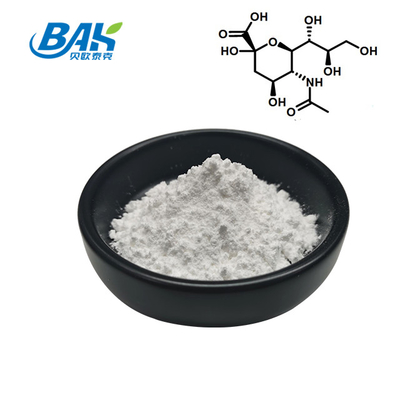
Wholesale Factory Supply Sialic acid Bird's Nest Acid Powder Birds Nest Extract
Product Details:
| Place of Origin: | Shaanxi China |
| Brand Name: | BAK |
| Certification: | HALAL, KOSHER, HACCP,ISO |
| Model Number: | 230815 |
Payment & Shipping Terms:
| Minimum Order Quantity: | 1kg |
|---|---|
| Price: | Contact the corresponding salesman |
| Packaging Details: | 1kg/bag,25k/drum |
| Delivery Time: | 5-8 work days |
| Payment Terms: | L/C, T/T, Western Union, MoneyGram |
| Supply Ability: | 1 Ton |
|
Detail Information |
|||
| Product Name: | Sialic Acid | Type: | Cosmetic Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance: | White Powder | Specification: | 98% |
| Packing: | 1kg/bag,25k/drum | CAS: | 131-48-6 |
Product Description
Wholesale Factory Supply Sialic acid Bird's Nest Acid Powder Birds Nest Extract
Product introduction:
Sialic acid is a type of sugar molecule that is widely distributed throughout the body and plays important roles in various biological processes. Here is some basic information about sialic acid:
Structure and Classification: Sialic acid is a derivative of the nine-carbon sugar neuraminic acid. It consists of a carboxyl group, an amine group, and a nine-carbon backbone. Sialic acid is classified as a negatively charged monosaccharide due to the presence of the carboxyl group.
Occurrence: Sialic acid is found in high concentrations on the outer surfaces of cells, especially on the terminal ends of glycoproteins and glycolipids. It is most commonly associated with cell surface molecules, such as glycoprotein receptors, where it plays a role in cell-cell recognition and communication.
COA of Sialic Acid
| Product Name | Sialic acid | |
| Item of Test | Limits of Test | Results of Test |
| Appearance | White powder | Complies |
| Assay | ≥98%(HPLC) | 99.5% |
| Odor | Characteristic | Complies |
| Loss on drying | <5% | 1.35% |
| Ash | <5% | Complies |
| Residual solvents | Negative | Complies |
| Residual pesticides | Negative | Complies |
| Chemical analysis | ||
| Heavy Metal | <10ppm | Complies |
| Arsenic (As) | <1ppm | Complies |
| Lead(Pb) | <1ppm | Complies |
| Cadmium (Cd) | <1ppm | Complies |
| Mercury (Hg) | Absent | Complies |
| Microbiology analysis | ||
| Total Plate Count | <1000cfu/g | Complies |
| Yeast & Mold | <100cfu/g | Complies |
| E.Coli | Negative | Complies |
| S. Aureus | Negative | Complies |
| Salmonella | Negative | Complies |
| Pesticides | Negative | Complies |
| Conclusion | Conform with specification | |
Product Function:
-
Cell Recognition and Signaling: Sialic acid residues on the outer surfaces of cells, especially on glycoproteins and glycolipids, are involved in cell recognition and signaling. They act as recognition markers for cell-cell interactions, allowing cells to identify and communicate with each other. Sialic acid interactions are crucial for processes such as immune response, cell adhesion, migration, and embryonic development.
-
Protection and Lubrication: Sialic acid molecules provide a protective function on cell surfaces. They form a negatively charged barrier that shields cells from enzymatic degradation and unwanted interactions. This protective role helps maintain the integrity and functionality of cell membranes. Additionally, sialic acid contributes to the lubrication of mucus and other body fluids, reducing friction and facilitating movement in various physiological processes, such as in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts.
-
Viral and Bacterial Interactions: Sialic acid can act as a receptor or binding site for certain viruses and bacteria. Some pathogens exploit sialic acid residues on host cell surfaces to attach to and enter cells. By recognizing and binding to sialic acid, pathogens can gain entry into host cells, leading to infection and disease.
-
Brain Development and Function: Sialic acid is crucial for proper brain development and function. It plays a role in neuronal growth, synaptic plasticity (the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time), and myelination (the formation of the protective myelin sheath around nerve fibers). Sialic acid modifications on glycoproteins are involved in neuronal signaling and neuronal cell adhesion, contributing to the formation and maintenance of neural connections and proper brain function.
-
Immune System Regulation: Sialic acid is involved in immune system regulation. It influences the activity of immune cells and the recognition of self and non-self antigens. Alterations in sialic acid patterns on cell surfaces can affect immune responses, including inflammation and immune cell activation.
-
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Sialic acid can exhibit anti-inflammatory effects by modulating immune responses. It can inhibit the activation of immune cells and the release of pro-inflammatory molecules, helping to regulate the inflammatory process.